| Lagging - planks or
split-round timber placed around timbered sets to keep material from falling into the
opening. Also used for flooring. |
 |
| Lamp - The electric cap lamp
worn for visibility. Also, the flame safety lamp used in coal mines to detect methane gas
concentrations and oxygen deficiency. |

|
| Lateral - a horizontal mine
working. |
|
| Layout - The design or pattern
of the main roadways and workings. The proper layout of mine workings is the
responsibility of the manager aided by the planning department. |
|
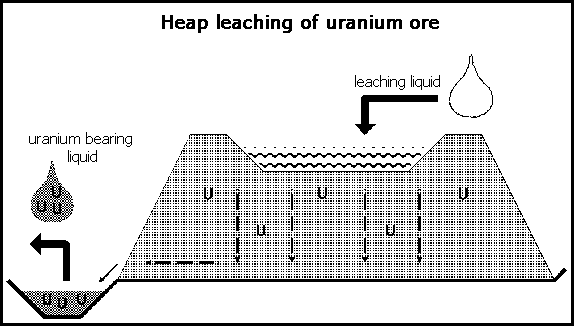
| Leaching - using chemicals or
solvents to win the valuable material from ore |
|
| Level - all the connected
horizontal mine openings at a certain elevation. |
|
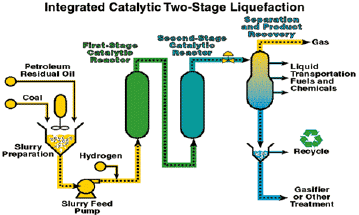
| Liquefaction – The
process of converting coal into a synthetic fuel, similar in nature to crude oil and/or
refined products, such as gasoline. |
 |
| Lithology - The character of a
rock described in terms of its structure, color, mineral composition, grain size, and
arrangement of its component parts; all those visible features that in the aggregate
impart individuality of the rock. |

|
| Load - To place explosives in
a drill hole. Also, to transfer broken material into a haulage device. |
|
| Loading machine - Any device
for transferring excavated material into the haulage equipment. |

|
| Loading pocket - Transfer
point at a shaft where bulk material is loaded by bin, hopper, and chute into a skip. |
 |
| Longwall Mining – One of
three major underground coal mining methods currently in use. Employs a steal plow, or
rotation drum, which is pulled mechanically back and forth across a face of coal that is
usually several hundred feet long. The loosened coal falls onto a conveyor for removal
from the mine. |

|
| Low voltage - Up to and
including 660 volts by federal standards. |
|