| Cage - In a
mine shaft, the device, similar to an elevator car, that is used for hoisting personnel
and materials. |

|
| Calorific value -
The quantity of heat that can be liberated from one pound of coal or oil measured in
BTU's. |
|
| Canopy - A
protective covering of a cab on a mining machine. |

|
| Cap - A miner's
safety helmet. Also, a highly sensitive, encapsulated explosive that is used to detonate
larger but less sensitive explosives. |

|
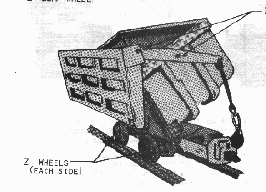
| Car - A railway
wagon, especially any of the wagons adapted to carrying coal, ore, and waste underground. |
|
| Car-dump - The
mechanism for unloading a loaded car. |

|
| Carbide bit - More
correctly, cemented tungsten carbide. A cutting or drilling bit for rock or coal, made by
fusing an insert of molded tungsten carbide to the cutting edge of a steel bit shank. |

|
| Carbon-in-leach: a
recovery process in which a slurry of gold ore, carbon granules and cyanide are mixed
together. The cyanide dissolves the gold content and the gold is adsorbed on the carbon.
The carbon is subsequently separated from the slurry for further gold removal. |

|
| Carbon-in-pulp:
similar to carbon-in-leach process, but initially the slurry is subjected to cyanide
leaching in separate tanks followed by carbon-in-pulp. Carbon-in-pulp is a sequential
process whereas carbon-in-leach is a simultaneous process. |

|
| Cast - A directed
throw; in strip-mining, the overburden is cast from the coal to the previously mined area. |

|
| Cave-in - the
partial or complete collapse of a mine working. |
|
| Caving System -
stoping systems designed to take advantage of the natural tendency of some ores to cave. |
|
| Certified -
Describes a person who has passed an examination to do a required job. |
|
| Chain conveyor - A
conveyor on which the material is moved along solid pans (troughs) by the action of
scraper crossbars attached to powered chains. |

|
| Chain pillar - The
pillar of coal left to protect the gangway or entry and the parallel airways. |
|
| Change house - A
special building constructed at a mine where the miners changes to his working clothes. |
|
| Chock - Large
hydraulic jacks used to support roof in longwall and shortwall mining systems. |

|
| Chute - An
inclined opening, usually constructed of timber and equipped with a gate, through which
ore is drawn from a stope into mine cars. |

|
| Claim - A portion
of mining land, usually 40 acres in size. |

|
| Coal - A solid,
brittle, more or less distinctly stratified combustible carbonaceous rock, formed by
partial to complete decomposition of vegetation; varies in color from dark brown to black;
not fusible without decomposition and very insoluble |

|
| Coal Gasification
– The conversion of coal into a gaseous fuel. |

|
| Coal washing
– The process of separating undesirable materials from coal based on differences in
densities. Pyritic sulfur, or sulfur combined with iron, is heavier and sinks in water;
coal is lighter and floats. |

|
| Coke – A
hard, dry carbon substance produced by heating coal to a very high temperature in the
absence of air. |
 |
| Collar - The term
applied to the timbering or concrete around the mouth or top of a shaft. The beginning
point of a shaft or drill hole at the surface. |

|
| Colliery - British
name for coal mine. |

|
| Column flotation
– A precombustion coal cleaning technology in which coal particles attach to air
bubbles rising in a vertical column. The coal is then removed at the top of the column. |

|
| Comminution - The
breaking, crushing, or grinding of coal, ore, or rock |

|
| Competent rock -
Rock which, because of its physical and geological characteristics, is capable of
sustaining openings without any structural support except pillars and walls left during
mining (stalls, light props, and roof bolts are not considered structural support). |
|
| Concentrate: a
powdery product containing the valuable ore mineral from which most of the waste material
has been eliminated. |

|
| Concentrator - A
particular type of milling plant that produces a concentrate of the valuable minerals or
metals. |

|
| Contact - The
place or surface where two different kinds of rocks meet. Applies to sedimentary rocks, as
the contact between a limestone and a sandstone, for example, and to metamorphic rocks;
and it is especially applicable between igneous intrusions and their walls. |

|
| Continuous miner -
A machine that constantly extracts coal while it loads it. This is to be distinguished
from a conventional, or cyclic, unit which must stop the extraction process in order for
loading to commence |

|
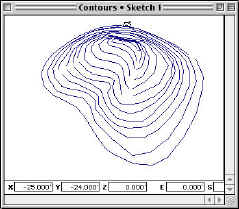
| Contour - An
imaginary line that connects all points on a surface having the same elevation. |
|
| Conventional mining
– The first fully-mechanized underground mining method involving the
insertion of explosives in a coal seam, the blasting of the seam, and the removal of the
coal onto a conveyor or shuttle car by a loading machine. |
|
| Conveyor - An
apparatus for moving material from one point to another in a continuous fashion. This is
accomplished with an endless (that is, looped) procession of hooks, buckets, wide rubber
belt, etc. |

|
| Convertor - A
furnace that is used to reduce metal from a matte. |
|
| Core sample – A
cylinder sample generally 1-5" in diameter drilled out of an area to determine the
geologic and chemical analysis of the overburden and ore. |

|
| Counterweight - A
dead or non-working weight attached to one end of a machine to balance the load carried on
the opposite end. |

|
| Country rock - A
term used to describe the general mass of rock adjacent to an orebody. |
|
| Cover - The
overburden of any deposit.
|

|
| Creep - The
forcing of pillars into soft bottom by the weight of a strong roof. In surface mining, a
very slow movement of slopes downhill. |

|
| Crib - A
roof support of prop timbers or ties, laid in alternate cross-layers, log-cabin style. It
may or may not be filled with debris. Also may be called a chock or cog. |

|
| Cribbing - The
construction of cribs or timbers laid at right angles to each other, sometimes filled with
earth, as a roof support or as a support for machinery. |

|
| Crossbar - The
horizontal member of a roof timber set supported by props located either on roadways or at
the face. |
|
| Crosscut - A
passageway driven between the entry and its parallel air course or air courses for
ventilation purposes. Also, a tunnel driven from one seam to another through or across the
intervening measures; sometimes called "crosscut tunnel", or
"breakthrough". In vein mining, an entry perpendicular to the vein. |

|
| Cross entry - An
entry running at an angle with the main entry. |

|
| Crusher - A
machine for crushing rock or other materials. Among the various types of crushers are the
ball mill, gyratory crusher, Handsel mill, hammer mill, jaw crusher, rod mill, rolls,
stamp mill, and tube mill. |

|
| Cut-and-fill: a
method of underground mining in which ore is removed in slices or lifts, and then the
excavation is filled with rock or other waste material (backfill) before the subsequent
slice is mined. |
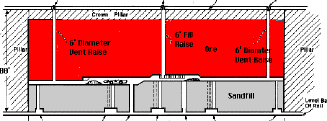 |
| Cut-off
grade - lowest
grade of ore in a deposit that will recover mining costs; the cut-off grade determines the
workable tonnage of an ore |
|
| Cutter; Cutting machine
- A machine, usually used in coal, that will cut a 10- to 15-cm slot. The slot
allows room for expansion of the broken coal. Also applies to the man who operates the
machine and to workers engaged in the cutting of coal by prick or drill. |

|
| Cyanidation: a
method of extracting gold or silver by dissolving it in a weak solution of sodium cyanide. |

|
| Cycle mining - A
system of mining in more than one working place at a time, that is, a miner takes a lift
from the face and moves to another face while permanent roof support is established in the
previous working face. |
|