| Decline - an inclined shaft
mined downwards (as opposed to an incline) |

|
| Deformation - change of the shape of a body by the action of a
force or stress |
|
| Demonstrated reserves –
A collective term for the sum of coal in both measured and indicated resources and
reserves. |
|
| Density - the mass
of a substance expressed in units of weight per unit volume |
|
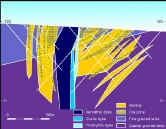
| Deposit - Mineral
deposit or ore deposit is used to designate a natural occurrence of a useful mineral, or
an ore, in sufficient extent and degree of concentration to invite exploitation. |
|
| Depth - The word
alone generally denotes vertical depth below the surface. In the case of incline shafts
and boreholes it may mean the distance reached from the beginning of the shaft or hole,
the borehole depth, or the inclined depth. |
|
| Detectors -
Specialized chemical or electronic instruments used to detect mine gases. |

|
| Detonator - A
device containing a small detonating charge that is used for detonating an explosive,
including, but not limited to, blasting caps, exploders, electric detonators, and delay
electric blasting caps. |

|
| Development mining
- Work undertaken to open up ore reserves as distinguished from the work of actual ore
extraction. |
|
| Diamond drill - A
rotary drill in which the cutting is done by abrasion rather than percussion. |

|
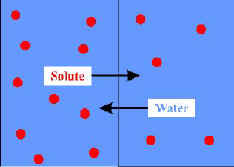
| Diffusion -
Blending of a gas and air, resulting in a homogeneous mixture. Blending of two or more
gases. |
|
| Diffuser fan - A
fan mounted on a continuous miner to assist and direct air delivery from the machine to
the face. |
|
| Dilute - To lower
the concentration of a mixture; in this case the concentration of any hazardous gas in
mine air by addition of fresh intake air. |

|
| Dilution - The
contamination of ore with barren wall rock in stopping. |
|
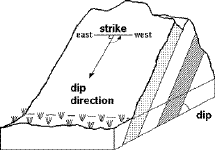
| Dip - The
inclination of a geologic structure (bed, vein, fault, etc.) from the horizontal; dip is
always measured downwards at right angles to the strike. |
|
| Dragline – A
large excavation machine used in surface mining to remove overburden (layers of rock and
soil) covering a coal seam. The dragline casts a wire rope-hung bucket a considerable
distance, collects the dug material by pulling the bucket toward itself on the ground with
a second wire rope (or chain), elevates the bucket, and dumps the material on a spoil
bank, in a hopper, or on a pile. |

|
| Drainage - The
process of removing surplus ground or surface water either by artificial means or by
gravity flow. |
 |
| Drift - A
horizontal passage underground. A drift follows the vein, as distinguished from a crosscut
that intersects it, or a level or gallery, which may do either. |

|
| Drift mine –
An underground mine in which the entry or access is above water level and generally on the
slope of a hill, driven horizontally into a orebody. |
|
| Drill - A machine
utilizing rotation, percussion (hammering), or a combination of both to make holes. If the
hole is much over 0.4m in diameter, the machine is called a borer. |

|
| Drilling - The use
of such a machine to create holes for exploration or for loading with explosives. |

|
| Driving - the
process of advancing a mine working, especially a drift or raise. |
|
| Dummy - A bag
filled with sand, clay, etc., used for stemming a charged hole. |
|
| Dump - To unload;
specifically, a load of coal or waste; the mechanism for unloading, e.g. a car dump
(sometimes called tipple); or, the pile created by such unloading, e.g. a waste dump (also
called heap, pile, tip, spoil pike, etc.). |

|














